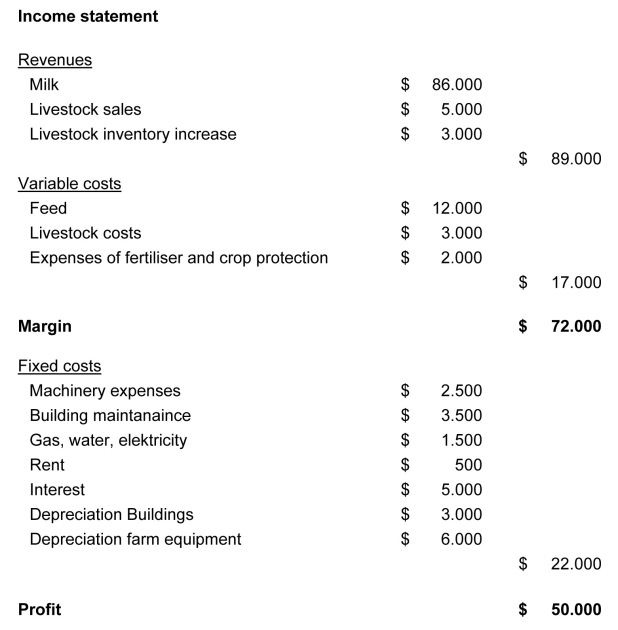
Profit and loss account
Revenues
A profit and loss account usually starts with a statement of the different revenues (or sales or turnover).
Costs
Costs can be calculated costs only or consist of real expenses (cash outflows). Depreciation is an example of an calculated cost without a cash outflow. Feeding costs and veterinary costs are examples of costs which are real expenses which result in a cash outflow.
Variable costs
Variable costs (also called allocated costs or expenses) are costs which are dependent of the production. When the production increases or decreases the variable costs will change as well. In case the production is stopped the costs will stop as well.
Fixed costs
Fixed costs (also called non-allocated costs) are those costs which are independent of the production of the enterprise. In case the production increases or decreases the fixed costs remain the same. In case the production is stopped theses costs will not stop automatically.
Gross margin
Revenues minus variable costs result in a gross margin. In case the gross margin includes only milk production it's expressed as gross margin milk. In case it includes also other production activities it's expressed as gross margin farm.
Depreciation and amortization
Depreciation and amortization represent the decrease in value of the fixed asset. Depreciation and amortization are costs but don't result in a cash outflow. Amortization is a term used for intangible fixed assets. Depreciation is a term used for tangible fixed assets.
Profit
Gross margin farm minus fixed costs, paid interest and amortization and/or depreciation result in profit (EBT...). Based on the profit the amount of tax to be paid to the government (Dutch situation) is calculated.
Savings
Profit minus tax paid results in savings.
Reserve capacity
Reserve capacity is the amount of money available to repay loans or to do (replacement) investments. It's calculated by net cash flow minus tax. This is a specific value only used by specific organisations.
Liquidity
Liquidity is the amount of money remaining from the reserve capacity after repayments and (replacement) investments are done. It's calculated by reserve capacity minus investments paid with available cash and repayments.
Gross cash flow
The gross margin minus the fixed costs result in a gross cash flow (EBITDA...).
Net cash flow
The gross cash flow minus the interest paid for liabilities result in the net cash flow (EBTDA...).